Origin and Evolution of Birds
Consider for a minute the diversity of birds. There are nearly 10,000 species! Is it possible to trace these birds back to one common ancestor? If so, who is it?
One of the major criticisms of Darwin’s Origin of Species was
the apparent lack of any evidence showing the evolution of birds. Then,
as luck might have it, only two years after he first published his book,
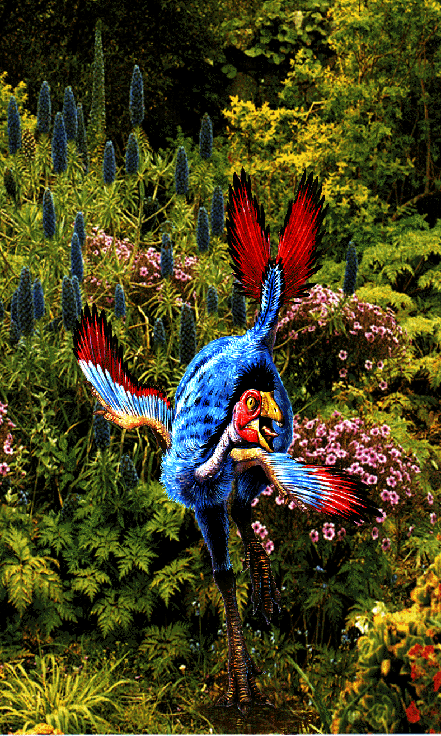
Archaeopteryx appeared in a site in Germany.
Today there are 8 preserved fossils of Archaeopteryx in various
museums of the world. What an amazing find for science because it stirred
scientists to try to figure out how birds were related to other creatures.
Archaeopteryx
was amazing for a few reasons. First it superficially resembled both a
bird and a reptile. In fact, except for the feathers, the
bird-like feet, and the fact that it had a wishbone
(furcula) it didn’t really look like a bird. The jaws
had teeth in them, of which no bird today has teeth. It also
had the ankle bone fused to the shinbone. Clearly this
bird had features of dinosaurs AND birds. So where did birds evolve?
Three hypothesis on origin of birds finally arose:
- Therapod dinosaur hypothesis: The first was a hypothesis
that they came from the therapod dinosaurs. Therapods are meat eating
dinosaurs such as Allosaurus. - Crocodiles – the second hypothesis was that they
came from crocodiles because they had an endolymphatic duct. Yet, as
more research was conducted, they discovered that there was a tremendous
amount of variation in this duct even among the lizards and other reptiles.
Not many people today give much attention to this hypothesis - Neither crocodiles or dinosaurs:Neither on the dinosaur
line or the crocodile line. Reasoning because several dinosaurs were
very specialized already.
Today we can show that birds are related in many ways to Dinosaurs. By
using key characters we can use cladistics to understand better the relationships.
For instance we can look at features they share in common with animals
such as reptiles, and ancient dinosaurs in order to figure out where they
may have evolved. They can thus, be linked generally to Ornithodira
and more specifically to Manirapterans.
If you look at a cladogram
of Diapsids which includes snakes, lizards, crocodiles (archosaurs),
and dinosaurs and birds, you can get a better picture as to where birds
fit in.
Dinosaur cladogram:
Looking in particular at the Ornithodira, Dinosaurs, Saurischian
dinosaurs, Therapods, Tetanurae, Coelesaurs, Manirapterans. (list
heirchial)
| Ornithodira | Advanced metatarsal ankle |
| Dinosauria | 3+ sacral vertebrae; reduced fibula |
| Ornithischia | 5+ sacral vertebrae, opptisthopubic pelvis, predentary bone in lower jaw |
| Sauropodomorpha | 10+ sacral vertebrae, ankles have an ascending process |
| Theropoda | Elongate, narrow metatarsus; hollow bones, metatarsal 5 reduced |
| Tetanurae | (Allosaurus etc.), has a tooth row on the upper row that does not extend back past the orbital (eyes). Also has a antorbital fanestra. |
| Maniraptora | because has a semi-opisthopedic pelvis. Means that the pubis bone of the pelvis is rotating backwards and has a foot. |
| Aviale | Presence of feathers |
Summarization of the set of derived characters that link them
to the dinosaurs:
• Pelvis
• Clavicles
• Wrist
Once the idea that birds came from dinosaurs began, there was a scurry
to find fossil evidence that could link birds back to their dino-roots.
Several different dino-birds arose in the last century. One was Caudipteryx
In China a fossil
was found that was dinosaur-like but had feathers. It seems that the wings
would have been too small to allow it to fly, but, the fact that it had
wings made it big news! Thus, the idea was that the initial evolution
of feathers may not have been for powered flight. In fact, if you look
at the tail feathers, it looks as though they are symmetrical around the
shaft. This finding forced a reconfiguration of the systematics of the
group.
Another fossil was found that, although it was not a fossil with wings,
it was a closely related dinosaur to birds that was very small and appeared
to be arboreal. This tiny fossil is only about 10 cm long and if it lived
in the trees could have glided from tree to tree.
ORIGIN OF FLIGHT.
How did it evolve?
For almost a century scientists have been debating this issue. The common
belief was that flight must have evolved from the trees down. This is
because every known modern semi-airborn animal (glider), seems to be arboreal.
Yet, another competing theory is that the wings are used to catch insects
and thus evolved from the ground up.
Leaping
One set of reasoning for the ‘ground-up‘ hypothesis is that dinosaurs
could have been leaping to catch insects and wings allowed them to come
down in one piece. Part of the evidence is that the capturing of prey
was the same movement for flight.
Wing-Assisted Incline running. (copy
of the study).
In a 2003 article in science, Kenneth Dial proposed his theory of ‘wing-assisted
incline running’ as a way for wings to evolve. In the study he used chucker
partridges and had them run up grades from 0 to 90 degrees. From 0 to
45 degrees, they just used their legs, but greater than 45 they used their
wings too. When they flap their wings, they put traction on the surface
and thus, increase their ability to run up the incline
Links about Bird Evolution and the Evolution of flight:
By Rob Nelson