Coast Redwood
Sequoia sempervirens
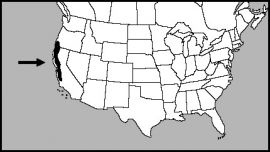
Redwood trees are not only the largest plants in the world, they are the tallest trees and the tallest living organisms found on Earth! They can grow as high as 370 feet tall, and they’re found in the temperate coastal rain forests of Northern California and Oregon.
How old are Redwoods?
Redwood trees are some of the oldest living trees in the world. Some trees can live as long as 3000 years. (The oldest living trees in the world are the Bristlecone pine, and there are trees living today in the United Stated that are over 6000 years old!)
Redwood trees have been around for longer than that though. Fossil records show that ancient forests of Redwood trees have been living throughout most of North America for the last 100 million years. At that time Redwoods were growing alongside the dinosaurs. Since the climate has changed much over the last 100 million years, today’s redwood forests are restricted to the pacific coast of northern California and Southern Oregon where the climate is moist, fairly cool, and the winters are mild.
The name Redwood and Sequoia
The Latin name of the Coast Redwood is Sequoia sempervirens. Sempervirens means “Forever green” or “living forever.” Sequoia sempervirens are cone-bearing gymnosperms and evergreens. Coast Redwoods are related to two other Redwood species: the Giant Sequoia, Sequoiadendron giganteum, which is found in the mid-elevations of the central Sierra Nevada mountains of California, and the rare Dawn Redwood, Metasequoia glyptostroboides, from China.
Coast Redwood trees are some of the fastest growing conifers in the world. As they grow, old needles, cones, and branches fall to the ground and make up the forest floor. As the duff decomposes, nutrients are recycled back into the environment. The duff is also a habitat for a wide variety of fungus and mushrooms. These organisms are essential for making the decomposition of duff possible and also provide many of the forest plants the nutrients they need to survive. Some common forest plants that live under the tall branches of the redwoods are ferns, oxalis, understory trees, like Cascara, Tanbark Oak, California Bay, Western Hemlock, Sitka Spruce, Douglas Fir, and shrub like huckleberry, Salal, Gooseberry, and Elderberry.
Related Topics
Redwood trees are not only the largest plants in the world, they are the tallest trees and the tallest living organisms found on Earth! They can grow as high as 370 feet tall, and they’re found in the temperate coastal rain forests of Northern California and Oregon.
How old are Redwoods?
Redwood trees are some of the oldest living trees in the world. Some trees can live as long as 3000 years. (The oldest living trees in the world are the Bristlecone pine, and there are trees living today in the United Stated that are over 6000 years old!)
Redwood trees have been around for longer than that though. Fossil records show that ancient forests of Redwood trees have been living throughout most of North America for the last 100 million years. At that time Redwoods were growing alongside the dinosaurs. Since the climate has changed much over the last 100 million years, today’s redwood forests are restricted to the pacific coast of northern California and Southern Oregon where the climate is moist, fairly cool, and the winters are mild.
The name Redwood and Sequoia
The Latin name of the Coast Redwood is Sequoia sempervirens. Sempervirens means “Forever green” or “living forever.” Sequoia sempervirens are cone-bearing gymnosperms and evergreens. Coast Redwoods are related to two other Redwood species: the Giant Sequoia, Sequoiadendron giganteum, which is found in the mid-elevations of the central Sierra Nevada mountains of California, and the rare Dawn Redwood, Metasequoia glyptostroboides, from China.
Coast Redwood trees are some of the fastest growing conifers in the world. As they grow, old needles, cones, and branches fall to the ground and make up the forest floor. As the duff decomposes, nutrients are recycled back into the environment. The duff is also a habitat for a wide variety of fungus and mushrooms. These organisms are essential for making the decomposition of duff possible and also provide many of the forest plants the nutrients they need to survive. Some common forest plants that live under the tall branches of the redwoods are ferns, oxalis, understory trees, like Cascara, Tanbark Oak, California Bay, Western Hemlock, Sitka Spruce, Douglas Fir, and shrub like huckleberry, Salal, Gooseberry, and Elderberry.