Cottonmouth
Agkistrodon piscivorus
Only Aquatic Viper
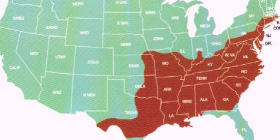
The cottonmouth, also known as the water moccasin, black moccasin and black snake, is the largest Agkistrodon species. It is a venomous pit viper that is found in the Southern and Eastern United States. It is more aggresive than the copperhead and is capable of giving a painful and potentially fatal bite. This is the world’s only semi-aquatic viper.
What does the Cottonmouth eat?
Cottonmouths are known for being one of the few venomous snakes that feed on fish. Their Latin name piscivorus means “fish eaters” from the roots piscis (fish) and voro (to eat). They generally feed on fish and frogs but will eat a wide variety of different animals that are present in their habitat.
Habitat of the Cottonmouth
Cottonmouths are almost always found in or around water, although they can be a substantial distance from a water body. The farthest we have found one is about a half a mile from a creek. They generally live in slow-moving water bodies, such as creek beds or shallow lakes. There have been reports of the snake entering seawater to colonize offshore islands in the Atlantic and Gulf coasts.
Related Topics
Only Aquatic Viper
The cottonmouth, also known as the water moccasin, black moccasin and black snake, is the largest Agkistrodon species. It is a venomous pit viper that is found in the Southern and Eastern United States. It is more aggresive than the copperhead and is capable of giving a painful and potentially fatal bite. This is the world’s only semi-aquatic viper.
What does the Cottonmouth eat?
Cottonmouths are known for being one of the few venomous snakes that feed on fish. Their Latin name piscivorus means “fish eaters” from the roots piscis (fish) and voro (to eat). They generally feed on fish and frogs but will eat a wide variety of different animals that are present in their habitat.
Habitat of the Cottonmouth
Cottonmouths are almost always found in or around water, although they can be a substantial distance from a water body. The farthest we have found one is about a half a mile from a creek. They generally live in slow-moving water bodies, such as creek beds or shallow lakes. There have been reports of the snake entering seawater to colonize offshore islands in the Atlantic and Gulf coasts.