Yellow Fever Mosquito
Aedes aegypti
Aedes aegypti is a vector for transmitting several tropical fevers. Only the female bites for blood, which she needs to mature her eggs. To find a host, these mosquitoes are attracted to chemical compounds emitted by mammals, including ammonia, carbon dioxide, lactic acid, and octenol.
The yellow fever mosquito can also contribute to the spread of reticular cell sarcoma among Syrian hamsters.
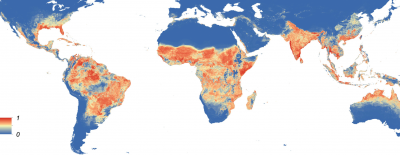
The mosquito carries a disease that is widespread in tropical South America and Africa, and often come out in moderate regions during the summer time. Today, the Aedes aegypti is found around the southeast region of the U.S., but is slowly decreasing due to competition with other mosquitoes, such as Aedes albopictus.
Related Topics
Aedes aegypti is a vector for transmitting several tropical fevers. Only the female bites for blood, which she needs to mature her eggs. To find a host, these mosquitoes are attracted to chemical compounds emitted by mammals, including ammonia, carbon dioxide, lactic acid, and octenol.
The yellow fever mosquito can also contribute to the spread of reticular cell sarcoma among Syrian hamsters.
The mosquito carries a disease that is widespread in tropical South America and Africa, and often come out in moderate regions during the summer time. Today, the Aedes aegypti is found around the southeast region of the U.S., but is slowly decreasing due to competition with other mosquitoes, such as Aedes albopictus.