Mammalia
What is a mammal?
The class Mammalia contains animals refered to collectively as mammals. Mammals include egg-laying species known as monotremes in addition to marsupials and placental mammals. There are several features that help define what a mammals is. These include the following:
- The presence of sweat glands (this includes sweat glands modified for milk production).
- Three middle ear bones that are used in hearing
- A neocortex region of the brain
Mammals are also defined as all descendants from the most common ancestor to the monotremes.
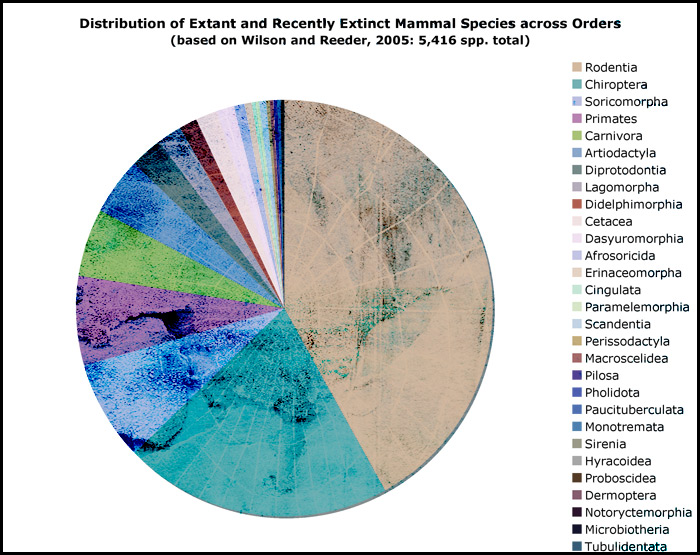
Mammal Abundance
There are about 5,400 species of mammals which are divided up into 153 families and approximately 1,200 genera. Mammals are currently undergoing a great deal of reorganization. Until this classification is universally accepted we have adopted the classifcation scheme most commonly adopted by mammology texts (that of Vaghan et al 2000)
Mammals as a group have done remarkably well, having taken over the planet after the age of the dinosaurs. One of the reasons for the great success of mammals is their ability to adapt to extremes of environments from hot regions to cold polar icecaps.
The most abundant mammal order contains the rodents. The second most abundant are the bats and the third most abundant are the shrews and moles (formerly Insectivora). The abundance of individual mammals can be displayed in the following pie chart which was produced according to the new classification of mammals.
Biggest and Smallest
The biggest mammal is the Blue Whale, which can reach 33 meters (110 feet) and weigh nearly 150 tons. The smallest mammal is the Bumblebee Bat which is only 30-40 millimeters.
Mammal Evolution
Mammals evolved from early reptilian-like ancestors. Modern mammals evolved from an ancestor of mammals. Many of the traits that are shared by mammals were likely adaptations to different conditions. For instance, the mammary glands that produce milk and help raise young were thought to have possibly evolved as a way to keep the eggs moist. Monotremes for instance to do not produce milk from nipples but instead secrete milk from their stomachs.
For more information on mammalian evolution please see these sites:
- Evolution of Mammals, a brief introduction to early mammals:
- Paleocene Mammals, a site covering the rise of the mammals:
For more Mammal information
- MAMMALOGY .org – The American Society of Mammalogists was established in 1919 for the purpose of promoting the study of mammals, and this website includes a mammal image library –