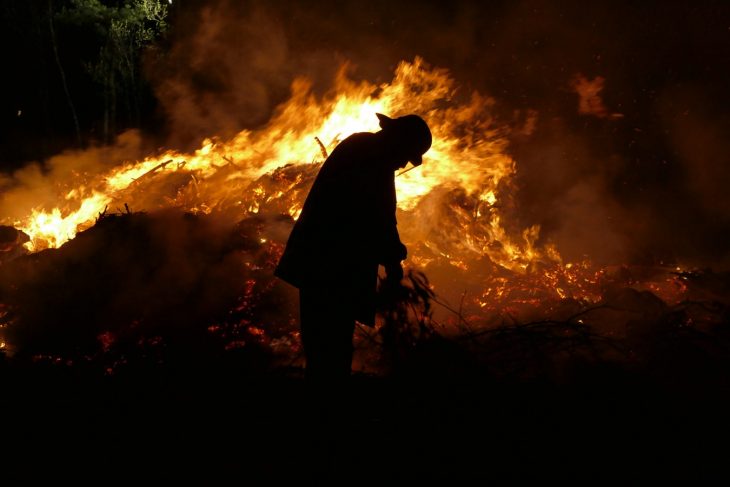
How Does a Wildfire Start?
Three elements are crucial for the creation of a wildfire: fuel, oxygen, and heat. Firefighters often refer to this combination of elements as the fire triangle. On a hot day, drought conditions peak and something as small as a spark has the potential to create a large wildfire with devastating consequences. Although fire can occur naturally from the sun or a lightning strike, most wildfires are started by human carelessness. Unextinguished campfires, lit cigarette butts, improperly burned debris, and arson are responsible for 84% of wildfires started. Man-made wildfires have tripled the fire season from 46 days to 154 days with a staggering cost of $2 billion. Once considered a natural phenomenon sparked by lighting, wildfires are now being recognized as the result of human error.

Harmful Effects of Wildfires
Wildfires can have immediate and long term effects on the quality of rivers, lakes, and streams. The most noticeable impact of wildfires is stormwater runoff. After the loss of vegetation, the ground’s soil becomes hydrophobic and prevents the absorption of water. This inability to absorb water promotes the transportation of debris and sediment into larger bodies of water, further polluting valuable and essential resources. Post-fire flash floods become a threat and allow the introduction of heavy metals from ash and soil to infiltrate waterways. Filtering these water sources can be costly as well as time consuming.
Depending on the temperature and time of year a wildfire occurs, vegetation can be significantly impacted. Plants on the forest floor or smaller trees are often destroyed by wildfires, while larger trees are able to survive as long as the fire does not spread into the tree canopy. The flames from these fires destroy the food source and homes of many animals, threatening their survival. For plants and trees that can survive the flames, they are susceptible to disease, fungus, and insects due to their decreased resistance following burn injuries.
Wildfires have both immediate and long-term impacts on air quality. As a forest burns, large amounts of smoke are released into the atmosphere. These smoke particles are typically small and made up of gases and water vapor. Air pollution from fires have the potential to travel great distances and oftentimes may pose a threat to human health. These small particles can become lodged deep within our lungs, making it difficult to breath as well as placing additional stress on our hearts. Additionally, wildfires produce an increased amount of carbon monoxide, which too can lead to a variety of health implications
Buildings and homes that lie within the path of a wildfire are destroyed, exposing hazardous materials that pose a threat on human health for first responders and during the clean up process. Older homes built before the 1970’s often contain a mineral called asbestos. Once asbestos is disturbed, the fibers become airborne and when inhaled can lead to the development of pleural mesothelioma in the lining of the lungs. During the cleanup process, many materials are often improperly disposed of and create a threat for destruction in the future. It’s important that these clean up processes are handled safely and completed with the proper equipment and done by a professional

The Ecological Benefits of Wildfires
Although wildfires leave an immense amount of destruction in their path, they do leave behind some beneficial qualities too. Many plants require regular burns in order to spread seeds and survive. Fires can also kill diseases and insects that may be affecting the livelihood of plants, remove excessive debris from the forest floor, and allow more access to the nutrients provided by exposed sunlight. Low intensity fires clear underbrush and prevent the damage of future fires from spreading.
After a wildfire, new grasslands are created and allow grazing animals to benefit from the change. This increase in the natural order of species allows a change in ecology that promotes growth and the continual cycle of life. Vegetation like the fireweed, requires the disturbance of fire to bloom and permit the regrowth of plants that have perished due to the fire. As plants and vegetation die away, new life begins to heal and spring forth.

What Can You Do
We’ve all heard the expression, “Only you can prevent forest fires.” Through taking preventative measures, we can assist in successfully eliminating, or decreasing the risk and number of wildfire outbreaks.
The first step in preventing a wildfire is never leaving a fire unattended. Completely extinguish a fire before sleeping or leaving the surrounding area. Be mindful of where you discard cigarettes, flammable liquids, and smoking materials and make sure they are never tossed on the ground. If you are hosting a fire, keep a shovel, water, and fire retardent nearby to prevent any possible chance of an untamed fire or outbreak.
If you do see an unattended or out-of-control fire, contact your local fire department and authorities as soon as possible. At the risk of a wildfire in your area, know your evacuation route ahead of time and keep a kit of emergency supplies ready. Before leaving your house, close all windows, vents, and doors to prevent a draft, remove all combustibles from your yard, and turn off any fuel oil supplies. Be sure to wear heat protective clothes to protect from sparks and ashes as well as a mask to shield your lungs from breathing in harmful fumes. For more information and preventative advice, visit the International Association of Wildland Fire here.
Unlike many natural disasters, most wildfires can be prevented. The environmental and economical costs of wildfires have an impact that lasts for many years. Through using caution, taking preventative measures, and monitoring fires responsibly, we can lower the threats associated with these devastating tragedies.
Learn More About Wildfires